| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
Tags
- monotone stack
- withContext
- cancellationException
- hotStream
- ServerDrivenUI
- TOSS 과제
- Advanced LCA
- ShapeableImageView
- Algorithm
- java
- coroutinescope
- SDUI
- 백준2309
- Android
- flowon
- KAKAO
- Next Challenge
- collectLatest
- Product Flavor
- Flow
- coroutinecontext
- coldStream
- app-distribution
- 백준
- conflate
- 릴리즈 키해시
- coroutine
- Kotlin
- google play console
- 안드로이드
Archives
- Today
- Total
루피도 코딩한다
[Flow Basics 2] Flow Intermediate and Terminal Operators 본문
Intermediate flow operators
Basic Operators
map: map 내부에서 변경한 데이터를 downStream으로 흘려보냄filter: 조건에 맞는 것만 남기기 (조건을 술어 혹은 predicate라고 한다)filterNot: 조건에 맞지 않는것만 남기기
Transform Operator
transform: stream 수정 (임의의 값을 임의의 횟수만큼 emit 가능)
Size-limiting Operators
take(n): 시작지점부터 n개만큼 data를 다 받아들이면 flow 실행 cancle 시키기takeWhile: 특정 조건을 만족하는 동안만 값을 가져오게 하기. 조건 안맞으면 즉시 실행 취소drop(n): 시작부터 n 개만큼 data 버리기- 만약 emit된 개수보다 n이 더 크다면 정상종료 됨
dropWhile: 특정 조건을 만족시키는 동안만 data 버리기.- 만약 첫번째 조건이 안맞았다 그러면 아무것도 안버리고 다 collect 하게 됨
Terminal Flow Operators
Terminal Flow(종단 연산자)는 suspend function이며 단일값을 반환함으로써 flow를 끝낸다. (내부적으로 collect 호출함)
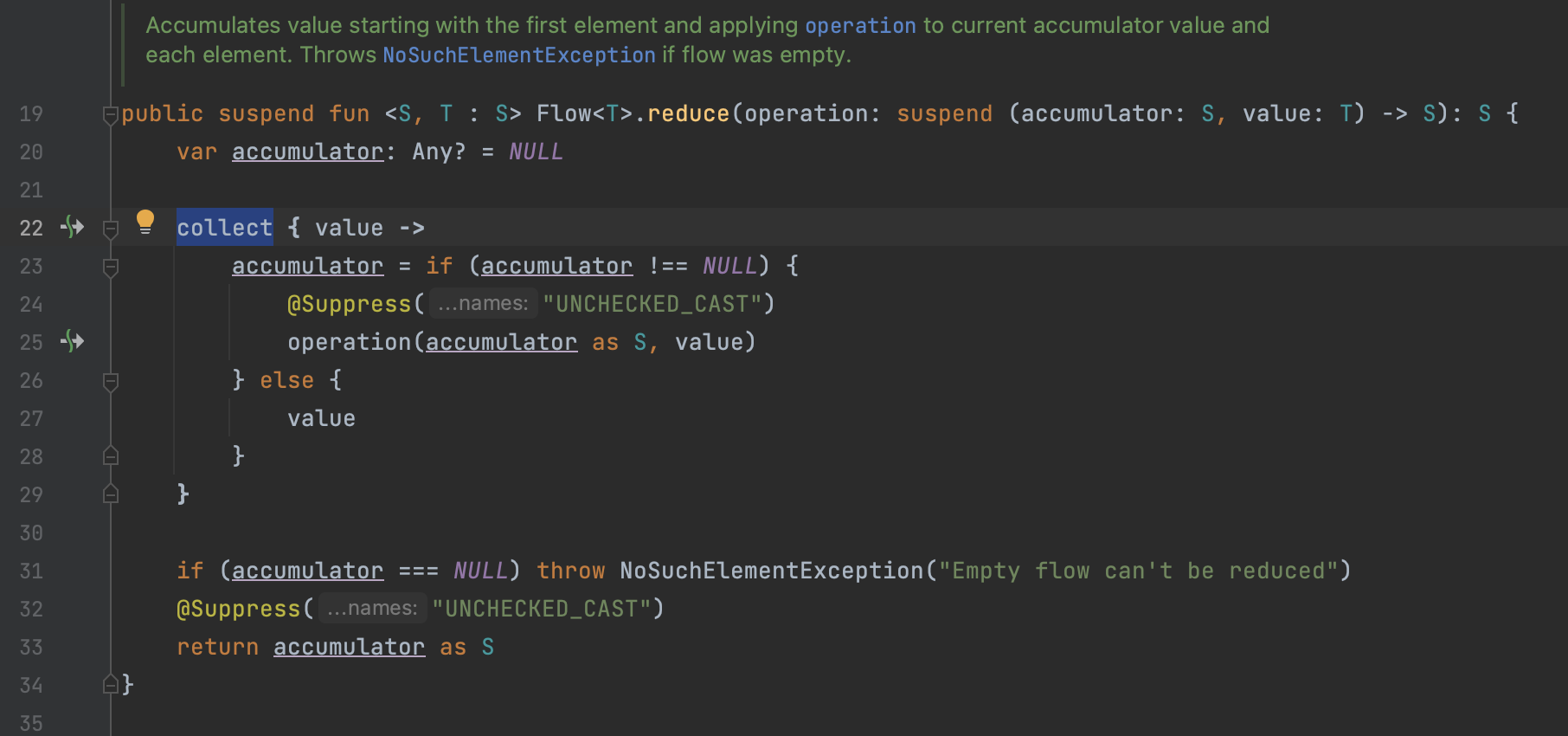
toList,toSet을 활용해 flow를 Collection으로 변형할 수 있다.first: flow의 첫번째 값 가져오기single: flow의 단일 값 가져오기. 만약 flow가 emit하는 데이터가 두 개 이상일 경우IllegalArgumentException발생reduce: collection을 누적해서 계산. 첫번째 데이터가 콜렉션의 첫번째 원소임.fold: collection을 누적해서 계산. 첫번째 데이터를 개발자가 직접 지정해주어야함.- cf. reduce와 fold는 Kotlin collection 기본 함수이기도 한데, 만약 해당 함수가 낯선 사람이라면 Kotlin 공식문서 예시를 보면 쉽게 이해할 수 있을것이다:)
count: count{ /* here(술어) */} 술어를 만족하는 자료의 개수 세기
Example of Operators
import kotlinx.coroutines.delay
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.*
import kotlinx.coroutines.runBlocking
fun flowSomething(): Flow<Int> = flow {
for (i in 0..20) {
emit(i)
delay(10L)
}
}
fun map() = runBlocking {
flowSomething()
.map { "$it $it" }
.collect { print("$it -> ") }
}
fun filter() = runBlocking {
flowSomething()
.filter { (it % 2) == 0 }
.collect { print("$it -> ") }
}
fun filterNot() = runBlocking {
flowSomething()
.filterNot { (it % 2) == 0 }
.collect { print("$it -> ") }
}
fun transform() = runBlocking {
flowSomething()
.transform {
emit(it)
emit(it * 2)
}.collect { print("$it -> ") }
}
fun take() = runBlocking {
flowSomething()
.take(5)
.collect { print("$it -> ") }
}
fun takeWhile() = runBlocking {
flowSomething()
.takeWhile { it == 3 }
.collect { print("$it -> ") }
}
fun drop() = runBlocking {
flowSomething()
.drop(21) // 0, 1, 2 이렇게 3개 버림
.collect { print("$it -> ") }
}
fun dropWhile() = runBlocking {
flowSomething()
.dropWhile { it % 2 == 0 }
.collect { print("$it -> ") }
}
fun toList() = runBlocking {
flowSomething()
.dropWhile { it % 2 == 0 }
.collect { print("$it -> ") }
}
fun toSet() = runBlocking {
flowSomething()
.dropWhile { it % 2 == 0 }
.collect { print("$it -> ") }
}
fun first() = runBlocking {
println(flowSomething().first())
}
fun single() = runBlocking {
println(flowOf("singleValue").single())
// println(flowOf("multipleValue", "occurException").single())
}
fun reduce() = runBlocking {
// 0, 1, .. 20 차례로 더하기
println(
flowSomething().reduce { accumulator, value ->
accumulator + value // sum of 0 to 20
}
)
}
fun fold() = runBlocking {
// 100, 0, 1, .. 20 차례로 더하기
println(
flowSomething().fold(100) { accumulator, value ->
accumulator + value // sum of 0 to 20, plus 100
}
)
}
fun count() = runBlocking {
// 홀수 몇개인지 세기
println(
flowSomething().count { it % 2 == 0 }
)
}
fun main(): Unit = runBlocking {
// map()
// filter()
// filterNot()
// transform()
// take()
// takeWhile()
// drop()
// dropWhile()
// first()
// single()
// reduce()
// fold()
count()
delay(1000)
}'Coroutine' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Flow Basics 4] Flow Buffering (1) | 2024.01.30 |
|---|---|
| [Flow Basics 3] Flow Context 핸들링 하는 방법 (0) | 2024.01.29 |
| [Flow Basics 1] Flow 기초(Flow Builder, Cold/Hot Stream) (0) | 2024.01.26 |
| [Coroutine Basics 7] Suspending function (1) | 2024.01.24 |
| [Coroutine Basics 6] Structured Concurrency, CoroutineScope, CoroutineContext (0) | 2024.01.22 |
Comments



